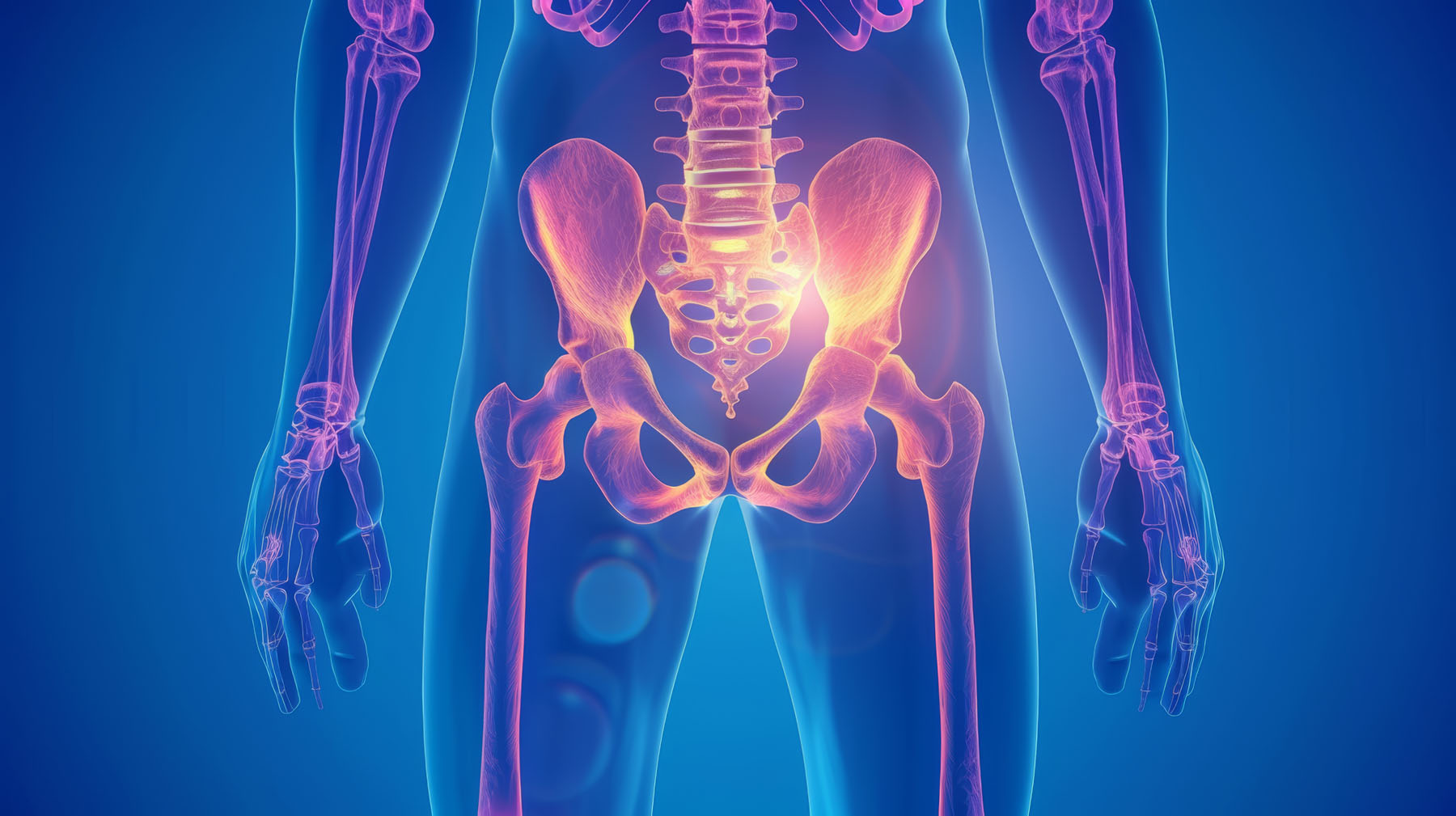
Pudendal nerve ablations are a medical procedure used to treat chronic pain originating from the area surrounding the pudendal nerve. The pudendal nerve is a crucial nerve that connects the spinal cord to the genitalia, perineum (the region between the genitals and anus), and anus, governing sensation and muscle control in the pelvic area, including functions like urination and defecation.
Pudendal neuralgia is a type of chronic pain associated with this nerve and it can impact individuals of any gender. It has various causes, including trauma during childbirth, pelvic surgeries like colorectal or gynaecological procedures, injuries to the pelvic or pudendal area (from falls or certain sports/exercises), or compression of the nerve due to tumours or infections.
Symptoms of pudendal neuralgia often include a spectrum of pain, ranging from mild itchiness to sharp shooting pains or persistent aches in the genital area, extending from the penis or vagina to the rectum. This discomfort can make sitting painful, with symptoms worsening throughout the day and typically improving at night.
At the Persistent Pain Solutions clinic, patients can find relief from pudendal neuralgia and chronic pelvic pain, with treatment options that include pudendal nerve ablation and pudendal nerve blocks.
Table of Contents
- What is Pudendal Nerve Ablation?
- How Does Pudendal Nerve Ablation Alleviate Chronic Pain?
- Why Would You Get a Pudendal Nerve Ablation for Chronic Pain?
- The Risks of Pudendal Nerve Ablation
- The Process of Getting a Pudendal Nerve Ablation
- Preparing for Pudendal Nerve Ablation
- After Getting Pudendal Nerve Ablation (Follow-Up)
- Finding a Doctor Who Performs Pudendal Nerve Ablations Near You
- Pudendal Nerve Ablations at Persistent Pain Solutions
What is Pudendal Nerve Ablation?
Pudendal nerve ablation is a medical procedure aimed at alleviating chronic pain associated with the pudendal nerve. This procedure involves using various techniques to selectively destroy or disrupt the function of the pudendal nerve, thereby reducing or eliminating the transmission of pain signals along the nerve pathways.
There are different methods used for pudendal nerve ablation, including:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) or Denervation (RFD) or Pulsed Radiofrequency (PRF) . With this approach, radiofrequency waves are used to disrupt the nerve’s ability to transmit pain signals. Radiofrequency Ablation is often performed under fluoroscopic guidance or CT guidance to ensure precise targeting of the nerve.
- Chemical Ablation. This method involves injecting a chemical agent, such as alcohol or phenol, directly into the area surrounding the pudendal nerve. The chemical agent damages the nerve fibres, blocking the transmission of pain signals.
- Cryotherapy. Cryotherapy involves using extreme cold to create lesions on the pudendal nerve. This is achieved by applying a freezing agent, such as liquid nitrogen, to the nerve, which destroys the targeted nerve fibres.
Pudendal nerve ablation is typically considered when more conservative treatments, such as medications, physical therapy, or nerve blocks, have been ineffective in managing chronic pelvic pain caused by conditions like pudendal neuralgia. It is often performed by interventional pain specialists or specially trained physicians in a hospital or outpatient setting.
As with any medical procedure, pudendal nerve ablation carries risks, including infection, bleeding, nerve damage, or unintended damage to nearby structures.
That said, pudendal nerve ablation can offer significant relief to patients suffering from chronic pelvic pain, improving their quality of life and restoring functional ability. However, the decision to undergo this procedure should be made in consultation with your doctor, weighing the potential benefits against the risks and considering your unique circumstances and treatment goals.
How Does Pudendal Nerve Ablation Alleviate Chronic Pain?
Pudendal nerve ablation aims to alleviate chronic pain by disrupting the transmission of pain signals along the pudendal nerve pathways. Here’s how it works:
- Disruption of Nerve Function. During pudendal nerve ablation, various techniques, such as pulsed radiofrequency ablation (RFA), chemical ablation, or cryotherapy, are used to selectively disrupt, damage or destroy the pudendal nerve fibres. This disruption interferes with the nerve’s ability to transmit pain signals from the pelvic region to the brain.
- Interrupting Pain Pathways. By creating lesions or damage to the pudendal nerve, pudendal nerve ablation interrupts the transmission of pain signals that contribute to chronic pelvic pain conditions like pudendal neuralgia. This interruption effectively reduces or eliminates the sensation of pain.
- Reduction of Inflammation.In some cases, pudendal nerve ablation may also help reduce inflammation in the surrounding tissues. Chronic inflammation can contribute to persistent pain in conditions like pudendal neuralgia, so by reducing inflammation, the procedure can provide additional relief beyond simply blocking pain signals.
- Long-term Pain Relief. Pudendal nerve ablation can provide long-term relief from chronic pelvic pain for some patients. By disrupting the function of the pudendal nerve, the procedure may result in sustained pain relief, allowing you to experience improved quality of life and functional ability.
- Complementary to Other Treatments. Pudendal nerve ablation can be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for chronic pelvic pain. It may be combined with other interventions such as medications, physical therapy, nerve blocks, or psychological therapies to optimise pain management and address the underlying causes of the pain.
Overall, pudendal nerve ablation offers a targeted approach to relieving chronic pelvic pain from pudendal neuralgia or other causes by disrupting the function of the pudendal nerve and interrupting the transmission of pain signals.
While the procedure can provide significant relief for many individuals, it’s essential to discuss the potential benefits, risks, and alternatives with your doctor before undergoing pudendal nerve ablation.
Why Would You Get a Pudendal Nerve Ablation for Chronic Pain?
Pudendal nerve ablation may be considered for chronic pelvic pain conditions like pudendal neuralgia, particularly when other conservative treatments have been ineffective in providing relief.
Here are several reasons why someone might undergo pudendal nerve ablation for chronic pain:
- Persistent Pain. If you experience chronic pelvic pain that significantly impacts your quality of life and daily functioning, despite trying various conservative treatments such as medications, physical therapy, or nerve blocks, pudendal nerve ablation may be considered as a potential option for long-term pain management.
- Pudendal Neuralgia. Pudendal neuralgia is a condition characterised by chronic pain originating from the pudendal nerve. If you have been diagnosed with pudendal neuralgia and experience severe or debilitating pain that affects your ability to perform daily activities, pudendal nerve ablation may be recommended to disrupt the transmission of pain signals along the affected nerve pathways.
- Failed Conservative Treatments. For patients who have not responded adequately to conservative treatments for chronic pelvic pain, such as medications or nerve blocks, pudendal nerve ablation may offer an alternative approach to pain management. By selectively damaging or destroying the pudendal nerve fibres, the procedure aims to provide long-lasting pain relief.
- Improved Quality of Life. Chronic pelvic pain can have a significant impact on various aspects of life, including work, relationships, and overall well-being. Pudendal nerve ablation may be pursued to improve quality of life by reducing or eliminating chronic pain symptoms, allowing individuals to resume activities they enjoy and participate more fully in daily life.
- Personalised Treatment Plan. Pudendal nerve ablation can be part of a comprehensive treatment plan for chronic pelvic pain, tailored to address the specific needs and circumstances of each patient. By combining multiple approaches, such as medications, physical therapy, and psychological support, with interventional procedures like pudendal nerve ablation, your pain management team can optimise pain management and improve overall outcomes.
It’s important to note that pudendal nerve ablation is not suitable for everyone with chronic pelvic pain, and the decision to undergo this procedure should be made in consultation with your doctor after careful consideration of the potential benefits, risks, and alternatives. Additionally, thorough evaluation and diagnostic testing may be necessary to confirm the underlying cause of the pain and determine if pudendal nerve ablation is appropriate.
The Risks of Pudendal Nerve Ablation
Pudendal nerve ablation, like any medical procedure, carries certain risks. While it can provide significant relief for chronic pelvic pain for many patients, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks and complications. Here are some of the risks associated with pudendal nerve ablation:
- Injection Site Reactions. Some patients may experience temporary pain, discomfort, or bruising at the injection site.
- Flare up of pain. There may be a temporary flare up of pain which is usually a ‘pressure effect’ from the injection.
- Infection. Any invasive procedure carries a risk of infection. Though rare, infection can occur at the injection site or in the surrounding tissues, leading to complications that may require further treatment. Signs of infection include increased pain, swelling, redness, or drainage from the injection site.
- Bleeding. There is a small risk of bleeding at the injection site, especially for patients taking blood-thinning medications. This can lead to hematoma (collection of blood) at the injection site.
- Allergic Reactions. Allergic reactions to the medications used in the injection, such as local anaesthetics or corticosteroids, are possible but uncommon. If a contrast dye is used during the procedure, there’s a slight risk of an allergic reaction to the dye, which may include rash, itching, or more severe reactions like anaphylaxis.
- Nerve Damage. While the goal of pudendal nerve ablation is to selectively damage or destroy the pudendal nerve fibres responsible for transmitting pain signals, there is a risk of unintended nerve damage. This can result in new or worsened symptoms, such as increased pain, numbness, or weakness in the pelvic region.
- Urinary or Bowel Dysfunction. Damage to the pudendal nerve or nearby structures during the ablation procedure may lead to urinary or bowel dysfunction, such as urinary retention, incontinence, or constipation. These symptoms may be temporary or permanent, depending on the extent of nerve damage.
- Sexual Dysfunction. Pudendal nerve ablation can potentially affect sexual function, particularly in men, by causing erectile dysfunction or altered sensation in the genital area. Women may also experience changes in sexual sensation or arousal as a result of nerve damage.
- Exposure to X-Rays and CT. Minimal doses of radiation are used to reduce the lifetime risk of long term complications (such as cancer) due to exposure to Xray and/ or CT scanning.
- Pain Persistence. In some cases, pudendal nerve ablation may not provide the desired pain relief or may result in persistent or recurrent pain symptoms. This can occur due to incomplete nerve destruction, nerve regeneration, or other factors contributing to chronic pelvic pain.
It’s essential to discuss all the risks and benefits of pudendal nerve ablation with your doctor. Ask Dr Meena Mittal and her team at the Persistent Pain Solutions all your questions and share any concerns before getting this or any other pain management procedure.
The Process of Getting a Pudendal Nerve Ablation
The process of getting a pudendal nerve ablation involves several steps and is typically performed by an experienced physician in a hospital or outpatient setting.
Here’s an overview of what to expect:
- Pre-procedural Evaluation. Before undergoing pudendal nerve ablation, you will have a thorough evaluation with your doctor. This may include a review of your medical history, a physical examination, and possibly diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies or nerve conduction tests, to assess the location and severity of your pelvic pain.
- Informed Consent. Your doctor will explain the pudendal nerve ablation procedure to you in detail, including its purpose, potential risks and benefits, and any alternative treatment options. You will have the opportunity to ask questions and discuss any concerns before providing informed consent to undergo the procedure.
- Preparation. On the day of the procedure, you may be asked to fast for a certain period of time before the scheduled appointment, especially if sedation or anaesthesia will be used. You may also be instructed to discontinue certain medications that could increase the risk of bleeding or interfere with the procedure.
- Anaesthesia. Depending on the specific technique used for pudendal nerve ablation and your individual preferences, you may receive local anaesthesia to numb the skin and tissues around the injection site, or you may be given sedation or general anaesthesia to help you relax and minimise discomfort during the procedure.
- The Procedure. Once you are adequately prepared and positioned on the examination table, your doctor will use imaging guidance, such as fluoroscopy (live X-ray) or ultrasound or CT, to precisely locate the pudendal nerve and ensure accurate placement of the ablation device or needle.
- Ablation. Using the chosen technique (e.g., radiofrequency ablation, chemical ablation, cryotherapy), your doctor will selectively disrupt or damage or destroy the pudendal nerve fibres responsible for transmitting pain signals. The ablation device or needle will be inserted into the target area near the pudendal nerve, and the procedure will be performed under real-time guidance to ensure optimal results.
- Post-Procedural Care. After the pudendal nerve ablation is completed, you will be monitored closely for a brief period in a recovery area to ensure there are no immediate complications or adverse reactions. Depending on the type of anaesthesia used and your overall condition, you may be discharged home on the same day or within a few hours.
- Follow-Up. Your healthcare provider will schedule a follow-up appointment to assess your response to the pudendal nerve ablation, monitor your pain relief, and address any concerns or questions you may have. Additional treatments or adjustments to your pain management plan may be recommended based on your individual needs and response to the procedure.
The process of getting a pudendal nerve ablation involves careful evaluation, informed consent, meticulous preparation, and skilled execution by a trained pain specialist. It’s important to communicate openly with your pain management team throughout the process and follow their recommendations for optimal outcomes.
Preparing for Pudendal Nerve Ablation
Preparing for Pudendal Nerve Ablation at the Persistent Pain Solutions clinic will require close communication with Dr Mittal and her team.
Be sure to disclose all medications you may be taking and note that you may have to discontinue some or all of them immediately prior to the procedure.
Prior to your appointment, please inform us if:
- You are currently taking antibiotics.
- You have a pacemaker or defibrillator.
- You have any allergies.
- You have diabetes.
- You are taking any blood thinning medications.
- You are feeling unwell, as we may need to reschedule your procedure.
For your safety, we recommend arranging transportation to and from your appointment, as driving yourself is not advised within the 24-hour period following the procedure.
We generally recommend you take leave from work on the day of the procedure and one day after the procedure, to rest and recover from the procedure.
If you are receiving pudendal nerve ablation, we advise you to refrain from undergoing any additional medical procedures, such as dental treatments or colonoscopies, within 48 hours before or after receiving a facet joint block.
Dr Meena Mittal and her team will provide specific guidance tailored to your situation. It’s important to adhere to your instructions diligently. If you have any concerns or queries, don’t hesitate to ask—we’re here to support you throughout the process.
After Getting Pudendal Nerve Ablation (Follow-Up)
Following the nerve ablation, you’ll undergo a brief resting period for observation and to allow the medication to work its effect. During this time, a member of Dr Mittal’s team will closely monitor you to ensure there are no unexpected side effects. You will likely be able to return the same day as getting the procedure.
Once the pudendal nerve ablation has been performed, you will be cleared to return home. A follow-up appointment will be scheduled to determine the next steps in your treatment plan.
Finding a Doctor Who Performs Pudendal Nerve Ablations Near You
For patients dealing with chronic pelvic pain, finding a pain specialist in Melbourne who can perform a pudendal nerve ablation is potentially life-changing.
Your general practitioner can provide a referral to a pain management clinic like Persistent Pain Solutions that offers pudendal nerve blocks and pudendal nerve ablations.
If you’re comfortable sharing your health concerns, you can also speak to family members, friends, or support groups (both online and in real life) for recommendations from those who have dealt with similar chronic pain issues.
Pudendal Nerve Ablations at Persistent Pain Solutions
Persistent Pain Solutions provides pudendal nerve blocks often followed by pudendal nerve ablations. These procedures are designed to alleviate chronic pelvic pain.
They target the pudendal nerves in your pelvic and genital area. Pudendal nerve ablation or denervation, which is also known as radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or pulsed radiofrequency (PRF). Ablation is a technique where a small portion of nerve tissue is incapacitated, which effectively interrupts pain signals to your brain. The result is often long-lasting relief from chronic pain.

Find a Persistent Pain Solutions Location Near You
Leader in Personalised Care, Integrative Pain Medicine, & Pain Management Intervention.
Pain Treatments We Offer in Melbourne, Victoria
Don’t Miss an Update
Join our newsletter to learn more about our staff, patients, and communities in the know on all of the recent news, events, and announcements for Persistent Pain Solutions.